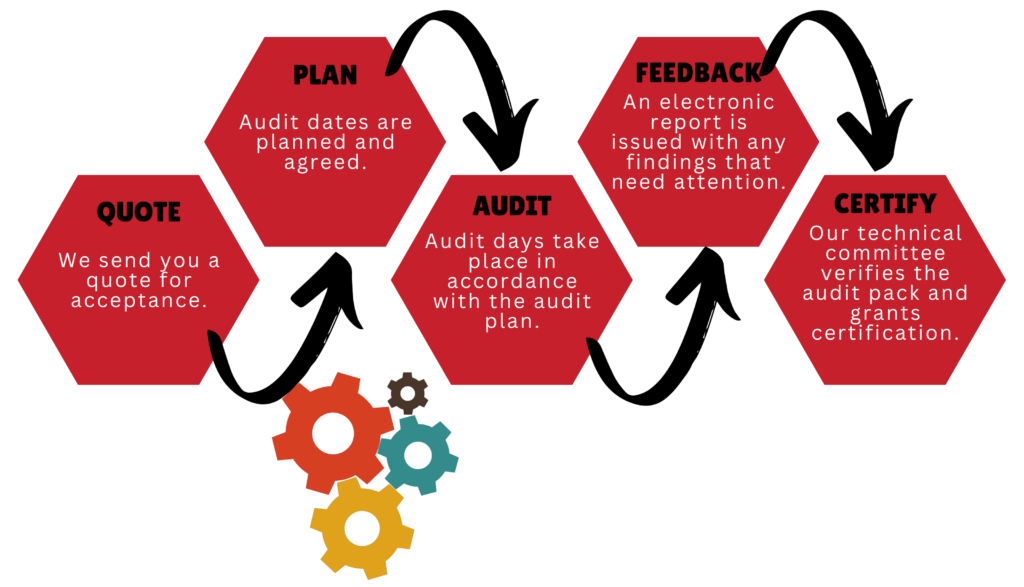
The Certification Process
Standards we assess and offer certification for:
“Quality is not an act, it’s a habit. With ISO 9001:2015, we make that habit a standard. Strive for excellence, efficiency, and customer satisfaction through the implementation of this industry-leading quality management system.”
ISO 9001:2015 is an international quality management system standard. It provides a framework for organisations to ensure that they consistently deliver high-quality products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Say what you do and do what you say is the basis of creating clarity and consistency.
The benefits of implementing ISO 9001:2015 QMS include:
- Improved customer satisfaction by consistently meeting their expectations.
- Increased efficiency and reduction of waste by implementing a process-based approach to managing all processes.
- Better risk management through a structured approach to identifying and addressing potential problems as well as applying risk treatment ideas to prevent negative risks.
- Improved communication and cooperation within the organisation through the entrenchment of clearly documented processes, checks and overall quality assurance.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility with customers, suppliers, and stakeholders once certification is achieved.
- Enhanced training programs can be realised.
- External and internal cost saving.
- Improved branding.
To implement ISO 9001:2015, an organisation must define and document its processes into a quality management system, train employees on its requirements, and continuously monitor and improve its performance. The key focus is on identifying risk, planning mitigation and continual improvement. The ISO 9001 management tools allows you to achieve this.
ISO 9001:2015 certification is a third-party endorsement that a company has implemented and is following the ISO 9001:2015 quality management system standards. The certification process involves an audit by an accredited certification body such as Sancert to verify that the organisation’s quality management system meets the requirements of the standard. Having the certification demonstrates to customers and other stakeholders that the organisation is committed to providing high-quality products and services at all times.
In order to effectively implement ISO 9001:2015 QMS the following should take place:
- Determine the scope of your quality management system (QMS) and identify the boundaries and the context of your organisation.
- Establish a QMS policy that outlines your organisation’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- Identify the processes that are critical to the success of your QMS and ensure that they are well-documented and communicated throughout the organisation.
- Assign responsibility for the implementation and maintenance of the QMS to a dedicated quality manager or a quality team.
- Develop a training program for employees to ensure that everyone understands their role in the implementation and maintenance of the QMS.
- Conduct a gap analysis to identify any gaps in your current QMS processes and procedures. Use risk-based thinking.
- Develop a detailed implementation plan to address the gaps identified in the gap analysis. Create a Risk register.
- Implement the processes and procedures of the QMS and monitor their effectiveness to ensure they are working as intended.
- Conduct regular internal audits to monitor the implementation of the QMS and identify areas for improvement.
- Establish a continuous improvement process to ensure that your QMS remains relevant and effective over time.
- Certification from a third-party certification body such as Sancert to demonstrate your commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
“Sustainability starts with you. With ISO 14001:2015, you make your commitment to the environment a standard, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future for all. Let’s work together to protect our planet and preserve it for generations to come.”
ISO 14001:2015 is an international environmental management system standard. It provides a framework for organisations to manage their environmental impacts and comply with environmental regulations. It also focuses on realising financial savings in reuse/reduce/recycling of products that affect your carbon footprint.
The benefits of implementing ISO 14001:2015 EMS include:
- Improved environmental performance by identifying and managing the organisation’s significant environmental impacts.
- Increased efficiency and cost savings through the identification and reduction of waste and the optimization of resource use.
- Better risk management by addressing potential environmental risks and liabilities.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility with customers, stakeholders, and regulators.
- Improved compliance with environmental regulations.
- Good environmental awareness.
To implement ISO 14001:2015, an organisation must define and document its environmental policy and objectives, identify its significant environmental impacts, implement controls to address them, and continuously monitor and review its performance.
ISO 14001:2015 certification is a third-party endorsement that a company has implemented and is following the ISO 14001:2015 environmental management system standards. The certification process involves an audit by an accredited certification body such as Sancert to verify that the organisation’s environmental management system meets the requirements of the standard. Having the certification demonstrates to customers and other stakeholders that the organisation is committed to providing products and services that have a minimal impact on the environment.
In order to effectively implement ISO 14001:2015 EMS the following should take place:
- Determine the scope of your environmental management system (EMS) and identify the boundaries and the context of your organisation.
- Establish an EMS policy that outlines your organisation’s commitment to environmental protection and sustainability.
- Conduct an environmental review to identify the environmental impacts of your operations and prioritise areas for improvement.
- Develop objectives and targets for your EMS that align with your organisation’s environmental policy and priorities.
- Assign responsibility for the implementation and maintenance of the EMS to a dedicated environmental manager or an environmental team.
- Develop a training program for employees to ensure that everyone understands their role in the implementation and maintenance of the EMS.
- Develop procedures for identifying, controlling, and monitoring environmental risks and impacts associated with your operations.
- Establish a process for identifying, evaluating, and managing environmental legal and regulatory requirements.
- Develop procedures for emergency preparedness and response to minimize environmental impacts in the event of an incident.
- Conduct regular internal audits to monitor the implementation of the EMS and identify areas for improvement.
- Establish a continuous improvement process to ensure that your EMS remains relevant and effective over time.
- Gain certification from an accredited third-party certification body such as Sancert to demonstrate your commitment to environmental protection and sustainability.
Process for carrying out an environmental aspect/impact study and planning environmental mitigation:
- Define the scope of the study. Determine the boundaries and context of the study, including the area of interest, and the purpose of the study.
- Identify potential environmental aspects: Conduct a thorough examination of the activities, products, and services of the organisation to identify potential environmental aspects that could impact the environment.
- Assess the significance of environmental aspects. Evaluate the significance of each environmental aspect by considering the extent and frequency of the impact and the sensitivity of the environment.
- Evaluate the environmental impacts: Analyse the environmental impacts of each aspect, including the direct and indirect impacts, and the positive and negative impacts.
- Develop an environmental impact matrix or register. Create an environmental impact matrix or register to condense the results of the impact assessment and to provide a basis for prioritising environmental mitigation measures.
- Plan environmental mitigation measures. Identify and prioritise environmental mitigation measures to reduce or eliminate the environmental impacts. This may include process changes, technology upgrades, waste minimization, and emissions reduction strategies as well as reuse and recycle processes.
- Implement the environmental mitigation measures. Develop an implementation plan for the environmental mitigation measures, including a timeline, budget, and resources required. Assign responsibility for implementation and monitoring to a dedicated environmental manager or team.
- Monitor and evaluate the environmental impacts. Regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the environmental mitigation measures and make any necessary adjustments to the plan.
- Report the results. Provide a written report of the results of the environmental aspect/impact study and the environmental mitigation plan. The report should be made available to stakeholders and interested parties.
“Safety is not just a priority, it’s a value. With ISO 45001:2018, you turn that value into a standard, ensuring the well-being of your employees, your customers, and your communities. Let’s strive for a safer future, one step at a time.”
ISO 45001:2018 is an international occupational health and safety management system standard. It provides a framework for organisations to manage their occupational health and safety risks and improve the well-being of their workers. It allows for a risk-based approach to consider possible risks and apply mitigation in order to reduce or eliminate risks prior to an incident. A preventive measure approach is used.
The benefits of implementing ISO 45001:2018 include:
- Improved occupational health and safety performance by identifying and managing workplace hazards and reducing the risk of workplace incidents.
- Increased efficiency and cost savings by reducing lost time due to accidents and illnesses.
- Better risk management by identifying and addressing occupational health and safety risks and liabilities.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility with customers, stakeholders, and regulators.
- Improved compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
- Effective programs for health and safety awareness.
To implement ISO 45001:2018, an organisation must define and document its occupational health and safety policy and objectives, identify its hazards and risks, implement controls to address them, and continuously monitor and review its performance.
ISO 45001:2018 certification is a third-party endorsement that a company has implemented and is following the ISO 45001:2018 occupational health and safety management system standard. The certification process involves an audit by an accredited certification body such as Sancert to verify that the organisation’s occupational health and safety management system meets the requirements of the standard. Having the certification demonstrates to customers and other stakeholders that the organisation is committed to providing products and services that have been manufactured and supplied in a safe and healthy manner.
Checks to carry out when implementing the ISO 45001:2018 Health and Safety management standard:
- Determine the scope of your Occupational Health and Safety management system and identify the boundaries and context of your organisation.
- Establish an Occupational Health and Safety policy that outlines your organisation’s commitment to providing a safe and healthy working environment.
- Conduct a hazard identification and assessment to identify potential health and safety risks and prioritise areas for improvement.
- Develop objectives and targets for your Occupational Health and Safety management system that align with your organisation’s health and safety policy and priorities.
- Assign responsibility for the implementation and maintenance of the Occupational Health and Safety management system to a dedicated health and safety manager or a health and safety team.
- Develop a training program for employees to ensure that everyone understands their role in maintaining a safe and healthy working environment.
- Develop procedures for identifying, controlling, and monitoring health and safety risks and hazards associated with your operations.
- Establish a process for identifying, evaluating, and managing health and safety legal and regulatory requirements.
- Develop procedures for emergency preparedness and response to minimize the potential impact of incidents on health and safety. Test these processes or procedures.
- Conduct regular internal audits to monitor the implementation of the Occupational Health and Safety management system and identify areas for improvement.
- Establish a continuous improvement process to ensure that your Occupational Health and Safety management system remains relevant and effective over time.
- Gain certification from a third-party certification body such as Sancert to demonstrate your commitment to providing a safe and healthy working environment.
Process methodology for doing a risk assessment on an organisation:
- Preparation- Determine the scope of the risk assessment and assemble a risk assessment team with appropriate expertise and knowledge of the organisation.
- Identification of risks- Identify potential risks to the organisation using a variety of methods such as brainstorming, process mapping, and data analysis.
- Assessment of risks- Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each identified risk and determine the overall level of risk for each.
- Rating and prioritisation of risks- Assign a numerical rating to each risk based on its likelihood and impact, and prioritise the risks based on their overall risk level.
- Risk treatment- Identify and evaluate options for treating each risk, including mitigation, transfer, and acceptance. Select the most appropriate risk treatment option based on the level of risk, available resources, and feasibility of implementation.
- Implementation- Develop and implement a plan to apply the selected risk treatment options, including monitoring and review processes.
- Continuous improvement- Regularly review and update the risk assessment process to ensure that it remains effective and relevant and identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
It is important to note that this methodology can be adapted to meet the specific needs and circumstances of each organisation and may require refinement based on the results of each risk assessment.
“Security is not an option, it’s a necessity. With ISO/IEC 27001:2022, we make that necessity a standard, protecting our sensitive information and safeguarding our assets. Let’s work together to ensure the safety of our data and the security of our future.”
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 is an international information security management system standard. It provides a framework for organisations to manage their information security risks and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information.
The benefits of implementing ISO/IEC 27001:2022 include:
- Improved information security by identifying and managing information security risks.
- Increased customer and stakeholder confidence in the security of their information.
- Better risk management by addressing potential information security risks and liabilities.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility with customers, stakeholders, and regulators.
- Improved compliance with data protection and privacy regulations.
To implement ISO/IEC 27001:2022, an organisation must define and document its information security policy and objectives, perform a risk assessment, implement controls to address the risks identified, and continuously monitor and review its performance.
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certification is a third-party endorsement that a company has implemented and is following the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 information security management system standards. The certification process involves an audit by an accredited certification body such as Sancert to verify that the organisation’s information security management system meets the requirements of the standard.
Check sheet for implementing ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security Management Standard:
- Define the scope of your information security management system (ISMS) and determine the boundaries and context of your organisation.
- Conduct a risk assessment to identify and prioritize information security risks, threats, and vulnerabilities.
- Develop an information security policy that outlines your organisation’s commitment to protecting sensitive information.
- Develop an ISMS framework and procedures that align with the information security policy and risk assessment findings.
- Assign responsibility for the implementation and maintenance of the ISMS to a dedicated information security manager or team.
- Develop a training program for employees to ensure that everyone understands their role in protecting sensitive information.
- Establish controls for the protection of sensitive information, including access controls, data backup, recovery procedures, and encryption methods.
- Implement a continuous monitoring process to detect, respond to, and prevent security incidents.
- Establish a process for responding to security incidents, including incident reporting, investigation, and remediation.
- Conduct regular internal audits to monitor the implementation of the ISMS and identify areas for improvement.
- Establish a continuous improvement process to ensure that your ISMS remains relevant and effective over time.
- Consider seeking certification from a third-party certification body to demonstrate your commitment to protecting sensitive information.
“Quality is the cornerstone of success in the world of medical devices and healthcare products. In a realm where precision and safety are paramount, ISO 13485 shines as a beacon of excellence.”
ISO 13485 is the international standard for quality management systems in the medical device industry. This standard is not just a set of guidelines; it’s a commitment to the highest levels of quality, ensuring that the products and services we rely on for our well-being meet the most stringent criteria. ISO 13485 isn’t just a certification; it’s a promise, a seal of approval that instills confidence in patients, practitioners, and manufacturers alike. Explore the world of ISO 13485, where quality and healthcare go hand in hand.
The benefits of implementing ISO 13485:2016 include:
- Regulatory Compliance: ISO 13485 aligns with regulatory requirements in many countries, making it easier for companies to demonstrate compliance and gain market access. This reduces the risk of product recalls and regulatory penalties.
- Improved Product Quality: The standard emphasizes a focus on product quality and safety, leading to better-designed and manufactured medical devices. This can result in fewer defects and, ultimately, improved patient safety.
- Enhanced Customer Confidence: ISO 13485 certification is a symbol of a commitment to quality, giving customers and stakeholders confidence in a company’s products and services. It can help build trust and long-term relationships with clients.
- Risk Management: ISO 13485 includes requirements for risk management processes, helping organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with their products. This reduces the likelihood of adverse events and liability issues.
- Efficient Processes: Implementing ISO 13485 promotes process efficiency and consistency within an organization. This can lead to cost savings, reduced waste, and improved resource utilization.
- Increased Market Access: Many countries and regions require ISO 13485 certification for medical device manufacturers to sell their products. Achieving this certification can expand market opportunities and increase the potential for international sales.
- Competitive Advantage: ISO 13485 certification can give companies a competitive edge in the medical device industry. It sets them apart as organizations dedicated to quality, which can be a significant selling point in a highly regulated and safety-critical sector.
- Continuous Improvement: The standard’s focus on continuous improvement encourages organizations to regularly assess their processes and make necessary enhancements. This leads to ongoing advancements in product quality and operational efficiency.
- Better Supplier Relationships: ISO 13485 certification often extends to suppliers in the medical device supply chain. This can improve the quality and reliability of raw materials and components, leading to higher quality end products.
- Legal and Liability Benefits: ISO 13485 can help organizations demonstrate due diligence in the event of legal disputes. It may also reduce liability by showcasing a commitment to safety and quality.
- Streamlined Documentation: The standard encourages structured and efficient documentation, making it easier to maintain records, manage changes, and communicate requirements throughout the organization.
- Employee Engagement: Employees in ISO 13485 certified organizations often have a better understanding of their roles, the importance of quality, and their contribution to the overall success of the organization. This can lead to greater job satisfaction and motivation.
ISO 13485 certification offers a comprehensive framework for quality management that not only ensures regulatory compliance but also leads to improved product quality, customer confidence, and overall business performance in the medical device industry.
“Corporate social responsibility is not a trend, it’s a commitment. With ISO 26000:2010, we turn that commitment into a standard, making a positive impact on society and the environment. Let’s be a responsible and sustainable business, one step at a time.”
ISO 26000:2010 is an international social responsibility standard. It provides guidance for organisations on how to operate in a socially responsible manner and consider the impact of their decisions and activities on society and the environment.
To implement ISO 26000:2010, an organisation must assess its social and environmental impact, develop a social responsibility policy and objectives, implement and monitor actions to improve its social and environmental performance, and engage with stakeholders to understand and respond to their needs and expectations.
The benefits of implementing ISO 26000:2010 include:
- Improved social responsibility by taking into account the impact of an organisation’s decisions and activities on society and the environment.
- Increased customer and stakeholder confidence in the organisation’s commitment to social responsibility.
- Better alignment of the organisation’s values and practices with social and environmental responsibility.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility with customers, stakeholders, and regulators.
- Improved risk management by considering the social and environmental risks and impacts of an organisation’s decisions and activities.
ISO 26000:2010 certification is a third-party endorsement that a company has implemented and is following the ISO 26000:2010 social responsibility standard. The certification process involves an audit by an accredited certification body such as Sancert to verify that the organisation’s quality management system meets the requirements of the standard.
When implementing this standard, the following key points should be considered:
- Stakeholder engagement- This involves engaging with stakeholders to understand their expectations and needs, and to build trust and transparency.
- Governance- This involves establishing a governance structure that provides leadership, direction, and management of the social responsibility program.
- Human rights- This involves ensuring that the organisation’s activities do not negatively impact human rights, and that the organisation is proactive in promoting and respecting human rights.
- Labour practices- This involves ensuring that the organisation’s practices are in line with international labour standards, and that workers are treated fairly and ethically.
- The environment- This involves ensuring that the organisation’s activities are environmentally sustainable, and that the organisation is proactive in protecting the environment.
- Fair operating practices- This involves ensuring that the organisation operates in a manner that is fair, transparent, and ethical, and that it avoids exploitation and corruption.
- Consumer issues- This involves ensuring that the organisation’s activities do not negatively impact consumers, and that the organisation is proactive in protecting consumer interests.
- Community involvement and development- This involves ensuring that the organisation’s activities are aligned with community interests, and that the organisation is proactive in supporting community development.
- Continuous improvement- This involves continuously improving the social responsibility program by monitoring performance, learning from experiences, and making necessary adjustments.
It is important to note that these key points are interrelated and should be integrated into the overall social responsibility program to ensure its effectiveness. Additionally, the standard should be applied in a way that is consistent with the organisation’s culture, structure, and operations.
“Risks are opportunities in disguise. With ISO 31000:2018, we turn those opportunities into a standard, managing risks and embracing challenges with confidence and success. Let’s face the future with resilience and assurance, one risk at a time.”
ISO 31000:2018 is an international risk management standard. It provides a framework for organisations to manage risk in a systematic and transparent manner, to ensure that their objectives are met and that they are prepared to respond to unexpected events. ISO 31000:2018 covers the entire process for managing risk in any standard applied be it ISO 9001, ISO 14001 or ISO 45001.
The benefits of implementing ISO 31000:2018 include:
- Improved risk management by identifying, assessing, and addressing risk in a systematic and transparent manner.
- Improved decision-making by considering risk in the decision-making process.
- Better alignment of risk management with the organisation’s objectives.
- Enhanced reputation and credibility with customers, stakeholders, and regulators.
- Improved resilience and preparedness to respond to unexpected events.
To implement ISO 31000:2018, an organisation must define and document its risk management policy and objectives, perform a risk assessment, implement controls to address the risks identified, and continuously monitor and review its performance.
ISO 31000:2018 certification is a third-party endorsement that a company has implemented and is following the ISO 31000:2018 risk management standard. The certification process involves an audit by a certification body such as Sancert to verify that the organisation’s ISO 31000:2018 risk management system meets the requirements of the standard.
The ISO 31000:2018 Risk management standard covers the following requirements:
- Establishing the risk management framework- This includes defining the scope of the risk management process, identifying stakeholders, and establishing roles and responsibilities.
- Risk assessment- This involves identifying, analyzing, and evaluating risks to determine their potential impact on the organisation.
- Risk treatment- This involves selecting and implementing appropriate strategies to manage risks, such as avoiding, reducing, transferring, or accepting risks.
- Monitoring and review- This involves regularly monitoring and reviewing the risk management process to ensure its effectiveness and making necessary adjustments.
- Communication and consultation- This involves engaging stakeholders and ensuring that risk management information is effectively communicated and shared throughout the organisation.
- Continual improvement- This involves continuously improving the risk management process by learning from experiences and making necessary adjustments.
It’s important to note that these key points are interrelated and should be integrated into the overall risk management process to ensure its effectiveness. Additionally, the standard should be applied in a way that is consistent with the organisation’s culture, structure, and operations.
Requirements for creating a risk methodology:
- Identify Risks: The first step is to identify all potential risks that could impact the organisation. This can be done through a variety of techniques such as brainstorming, risk assessments, and stakeholder engagement.
- Analyse Risks: Once the risks have been identified, they need to be analysed to determine their potential impact and likelihood. This can be done by using tools such as a risk matrix, which plots the likelihood and impact of each risk on a grid.
- Assess Risks: The next step is to assess the risks to determine their overall level of risk. This can be done by combining the likelihood and impact scores, and assigning a risk rating (e.g. high, medium, or low) based on the results.
- Prioritize Risks: Based on the risk ratings, the risks should be prioritized so that the most significant risks receive the highest level of attention. This will help the organisation focus its efforts on managing the risks that pose the greatest threat.
- Develop Risk Response Plans: For each prioritised risk, the organisation should develop a risk response plan that outlines the steps that will be taken to manage the risk. The plan should consider strategies such as avoiding the risk, transferring the risk, reducing the risk, or accepting the risk.
- Implement Risk Response Plans: The final step is to implement the risk response plans and monitor the risks to ensure that they are effectively managed over time. The risk management process should be ongoing, and the organisation should continually assess and update its risk response plans as needed.
It’s important to note that this is a simplified version of a risk methodology process, and organisations may choose to adapt or modify the process based on their specific needs and circumstances.







